Introduction
China boasts the second-vastest trade globally, characterised by rapid growth and development. Over the past few decades, it has transitioned from a manufacturing powerhouse to an innovation-driven economy. This shift has been fueled by robust infrastructure, a skilled workforce, and a favourable endeavour environment. The Chinese state continues to implement reforms aimed at opening up the market, luring multinational stakes, and fostering entrepreneurship.
The nation offers unparalleled potential for foreign endeavours. With a population greater than 1.4 billion, the demand for goods and services is immense. Urbanisation, rising incomes, and a growing middle class further enhance the market's attractiveness. Sectors such as technology, e-commerce, healthcare, and customer products are majorly ripe for investment. However, success requires an in-depth awareness of local consumer behaviour, statutory and adherence, and strategic collaborations.
Establishing an enterprise in China is a complex sequence that is followed by a number of lawful formalities. It is pivotal to take into account the specifics of financial regulation, levy specifications, and administrative nuances that have a significant impact on the success of launching your enterprise.
This review will discuss what essentials must be met to start a firm in China, and the types of legal entities available for registration by foreigners.
Business benefits in China
Due to its geographical territory, the opportunities offered by registering a Chinese company are unprecedented in the trade field. Due to its favorable position in the center of East Asia, the polity aids as a powerful manufacturing center and provides not only access to the trading fields of Europe, America, Africa and other regions, allowing for efficient trading operations and generating protracted partnerships, but also allows leverage of new opportunities for marketing products, expanding the customer base.
It also gives access to a large consumer market. The nation has developed transport and logistics networks. The jurisdiction has focused its efforts on promoting high-tech industries. These efforts include creating dedicated zones for technology startups, funding scientific projects, and supporting infrastructure for innovative enterprises.
Registering a company in China provides entrepreneurs with a number of additional advantages, incorporating:
- Authorities have cut bureaucratic barriers and reformed business regulations in China to make things easier for overseas endeavours.
- Some regions have SEZs and technology parks that offer levy preferences and other incentives for new and innovative companies.
- There is a significant potential for highly skilled talent, covering a broad scope of fields incorporating engineering, information technology and scientific research.
- Entrepreneurs who decide to register a company in China will have the opportunity to establish partnerships with local business entities, which can speed up market entry and increase competitiveness.
Challenges faced by foreign businesses in China
Transnational endeavours admitting the territory's market often encounter a span of challenges:
Mandarin Chinese is the primary language, and while English is increasingly spoken in trade circles, language barriers can still pose significant challenges. Effective communication is critical for negotiations, legal documentation, and daily operations.
China’s statutory environment can be difficult and is often contingent on changes. Navigating the intricate web of local, provincial, and national directives requires thorough understanding and constant vigilance. Compliance with these statutes is vital to hinder legislative challenges and sanctions.
Understanding and adapting to Chinese trade culture is vital. Practices such as giving and receiving face (mianzi), the importance of hierarchy, and indirect communication styles can differ greatly from Western norms. Misunderstandings in these areas can hinder trade negotiations and relationships.
Despite improvements in IP protection statutes, intellectual property theft remains a concern for transnational ventures. Ensuring robust IP protection strategies and being proactive in monitoring and enforcement is necessary to safeguard innovations.
The polity’s trading field is highly competitive, with both local and transnational players striving for market share. Local endeavours often have a better comprehension of consumer preferences and faster adaptation to market trends, presenting a significant challenge for newcomers.
The vast geographical expanse of China can create logistical challenges, incorporating transportation, delivery and logistics handling. Efficient logistics planning and partnerships with reliable local providers are essential to mitigate these issues.
Registration of a company in China by a non-resident: restrictions
Directives governing foreign investment in China incorporate various requirements, such as prior certification from the authorities and others. The main legislative act related to the regulation of business in China carried out by foreign entrepreneurs and endeavours is Foreign Investment Law (FIL).
The law stipulates that foreign trade entities have the same rights as national entrepreneurs with the caveat that they do not plan to function in one of the positions in the undesirable category. The percentage of foreign ownership in the sectors on this list varies. For example, banking activities completely prohibit foreign ownership. In other industries, 50% of the resources are authorised to be possessed by expats.
Contact a specialist to clarify your rights to an ownership interest in a specific sector. Our team specializes in comprehensive support in registering companies in China , and we also provide consultations for already operating enterprises.
How is a company registered in China ?
The detailed process of company registration in China is summarised below:
- Determination of the legislative form (based on the scale of the venture, quantity of founders and prepared tasks).
- Selection and approval of a unique trade name. The title does not infringe the rights of third parties and must comply with Chinese legal requirements.
- Enrollment of lawful address. To do this, you will be mandated to conclude a lease contract or provide other files certifying the presence of a legal address.
- Planning of constituent papers, incorporating the Charter, protocol on the creation of an organisation, identification indentures of the founders.
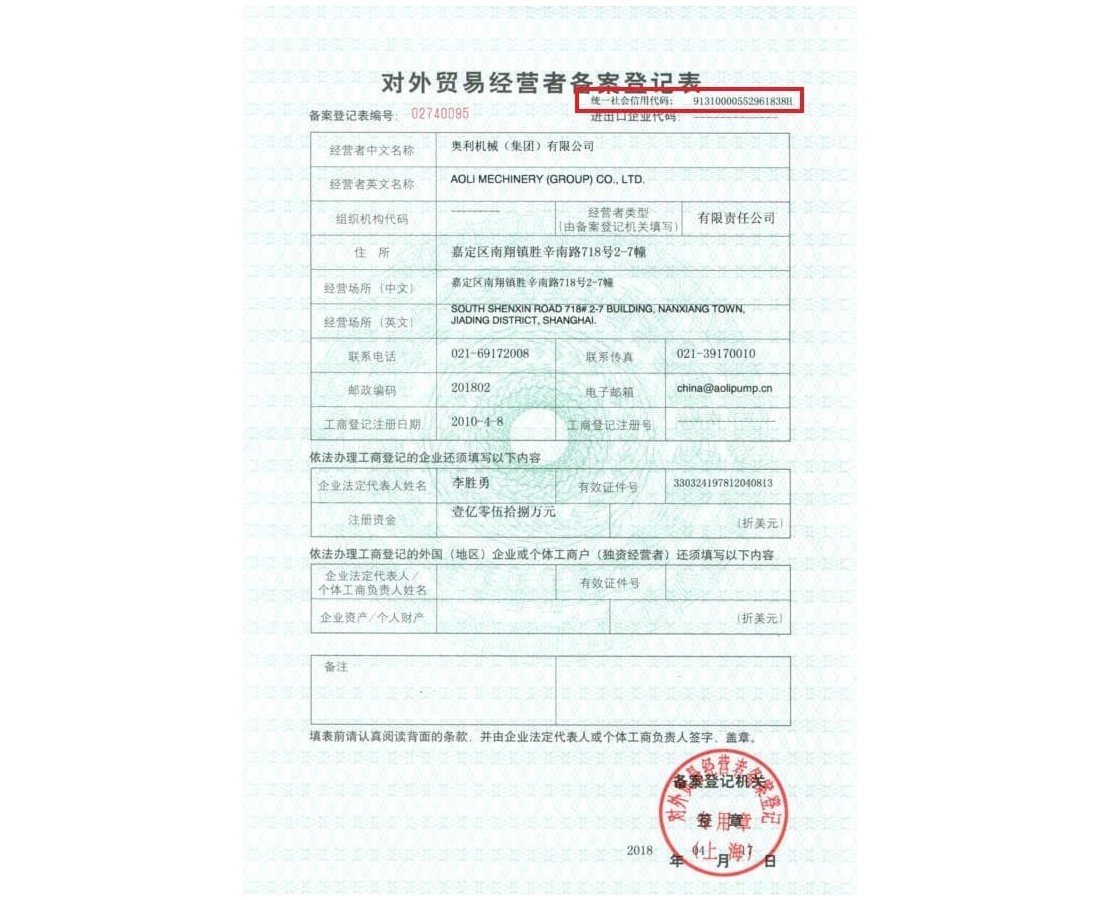
- Filling out a registration form (illustration below). The application must be signed by the founders or an authorized person.
- Payment of the public bill, the quantity of which relies on the chosen form and other factors.
- Submission of collected files and enrollments to the designated supervisor.
After successful verification of records, the Chinese registration authority issues a Company Registration Certificate . From this moment the organisation is officially identified and can begin its schemes. To conduct financial operations you are mandated to open an account in a Chinese bank . To do this, you will need documents proving the enrollment of the organisation and the administration of the persons entitled to dispose of the account.
It is obligatory to go through the registration procedure with the Chinese Tax Administration to obtain a TIN and be incorporated in the enrollment of levy payers. It is also important to apply for appropriate warrants to operate a trade. This process ensures that the trade has a lawful basis to function in accordance with regional regulations and asserts that your interests are protected.
Legal structures to open a company in China
There are several main types of legal structures to register an enterprise in China ( described in the table ).
|
WFOE |
Joint Venture |
RO |
Branch |
|
Registration of a WFOE in China gives foreign endeavours the right to conduct trade activities without the need to have a Chinese partner. The lawful distinction between WFOE resources and stakeholder holdings is clearly defined, providing a level of accountability protection. The decision to establish enterprises with 100% foreign capital in China gives its owners unlimited opportunities to move capital outside the country. The statutory framework of WFOE is directed by the FIL and its implementing regulations. These laws establish the conditions for the creation, scheme and dissolution of a WFOE, incorporating minimum reserve prerequisites and the need to create a board team or a single executive director. |
To enhance international economic cooperation and technology exchange, the Chinese government encourages the establishment of enterprises by Chinese and foreign parties. In a JV, at least two groups pool resources to accomplish a specific task, example, new project, or other trade activity. Each partner has some influence and responsibility for establishing ambitious plans and handling regular operations. Joint ventures are usually utilized by monetary backers to enter into restricted industries such as education, mining, banking, road construction, transportation, etc. This scheme can be especially beneficial for trades that mandate a combination of experience and capital. You can create a joint venture in China in the forms of LLC or JSC. |
The representative office of a foreign company in China is without opportunity to conduct commercial operations in this country. The RO can perform some functions such as marketing, market research and providing information about the products/support of the transnational corporation. |
Registration of a branch in China allows a foreign venture to carry out commercial operations in the local market. A branch is absent of a distinct legislative personality, but is an extension of an organization incorporated in another country. The branch mandates the appointment of an agent (a citizen of the People's Republic of China). The branch must pay applicable taxes in accordance with applicable rates and rules. |
Another form for registering a business in China is FIPE (Foreign-Invested Partnership Enterprise) or partnership enterprise with foreign capital. FIPE has the features of a partnership, where the participants share obligations and revenues in conformance with the partnership undertaking.
FIPE is a popular form among startups in China as it doesnt call for the mandatory payment of enrolled finance. FIPE types:
- General Partnership (GPE): Created by a minimum of two partners who have limitless combined and multiple liability for trade debts.
- Limited Liability Partnership (LPE): formed by combining overall and silent affiliates, the latter of whom are accountable for the loans of the collaboration to the degree of their resource sponsorship.
- Specialized General Partnership (SGPE): established to provide services that demand expert expertise and distinctive capabilities. This framework protects partners from liability arising from the purposeful misbehaviour or severe carelessness of one or more associates.
The choice of form is based on the strategy and mandates of the endeavour, equally the prerequisites governing the schemes of transnational firms in the polity. For advice, contact lawyers or consultants specialising in supporting international investment activities.
Registration of a legal entity in China in special zones
SEZs are geographically defined fields where unique rules and conditions apply to stimulate the progress of investment potential. There are several such zones in China (described below).
Opening a company in a free zone in China has certain preferences:
- Licit entities registered in special zones can receive a levy discount, which authorises them to reduce the levy base by a certain amount of income, exempting this part from taxation. This allows you to significantly reduce your levy liability.
- Enterprises in the FEZ are exempt from paying customs and import-export duties on goods moved between the FEZ and points abroad.
- SEZs apply simplified immigration clearance steps, which reduces time and pecuniary costs for customs formalities.
- Ventures whose operations involve transnational shipment, conveyance and storage might be relieved from remunerating revenue impost.
The Shanghai Free Trade Zone (SHFTZ) was officially launched on September 29, 2013. Registration of a company in the Shanghai Free Trade Zone is possible in sectors including biology, overseas trade, and monetary support.
The Shanghai FTZ covers a total area of 28.78 square meters. km. It consists of four strategically important zones:
- Waigaoqiao FTZ, located among the key fiscal regions of Shanghai. This zone is a center for innovative innovations and growth of new trade initiatives.
- Waigaoqiao Free Trade Logistics Park, which plays a key role in providing efficient logistics solutions to ventures operating in the transnational trading field. Modern facility capabilities and high-tech cargo management systems provide optimal conditions for transnational trade and distribution of goods.
- Yangshan FTZ, positioned near the largest port of Shanghai. It works as the main center for shipping and trade. Here ventures have access to a span of support related to maritime logistics.
- Pudong International Airport FTZ, located next to one of the biggest and most modern airports in the world. This zone provides fast and convenient access to air freight and logistics solutions.
Fujian FTZ, officially launched in 2015, covers a total area of 118.04 square kilometers and consists of three zones:
- Pingtan zone;
- Xiamen Zone (incorporating Xianyu Zone, Xianyu Logistics Park and Haicang Port);
- Fuzhou area (incorporating Fuzhou zone, Fuzhou free port and Fuzhou port).
The Fujian FTZ targets to become an transnational center for advanced manufacturing, innovative shipping, developed tourism, maritime route construction, fiscal invention and cooperation. The attention on these key areas highlights the strategic importance of the Fujian Free port in achieving sustainable advancement and growth perspectives for multinational cooperation.
The Guangdong FTZ, officially launched in April 2015, covers three areas with a total area of 116.2 sq. km:
- Nansha District in Guangzhou;
- Qianhai-Sekou district in Shenzhen;
- Hengqin Zhuhai District.
This zone is focused on creating direct maritime trade routes to Europe and Africa. It is designed to become a key node in the global trade network, driving the enhancement of an internationally connected financial sector, strengthening the manufacturing base and forming a hub for shipping and supply chains. The Guangdong FTZ attracts foreign direct investment into China in the areas of trade and technology.
This FTZ began to operate in Tianjin Municipality in 2015. The Tianjin Free Trade Zone consists of three territories with a total area of 119.9 sq. km:
- Dongjiang zone of Tianjin port;
- Tianjin Airport area;
- Binhai New Area Integrated Free Trade Zone and Binhai Central Business District.
Tianjin Free Trade Zone is the optimal place to register trading companies in China . Tianjin's proximity to Beijing, excellent transport links and a quantity of major Chinese ports make this area a preferred location for ventures involved in international trade.
Registration or purchase of a company in China: choosing an industry for capitalization
Opening a company in China provides unique opportunities in various sectors of the country's economy. Some main sectors in which foreigners are interested in doing trade are:
- Manufacturing and industry. PRC is known for its manufacturing potential and industrial base, offering opportunities for setting up manufacturing plants in various industries, like electronics, textiles, steel rolling, and construction tools.
- Technology services. The state devotes resources in expansion of research centers and technology parks. These investments help create favorable conditions for the growth of innovative ventures and start-ups. The result is a system that stimulates the advent of advanced techs and pulls talent. Thanks to this, innovative firms gain access to modern equipment, professional skill and the necessary infrastructure, which significantly accelerates their and the introduction of new products and services to the market.
- Information Technology. The country has seen a rapid drive in the need for enhancement of key industries such as Internet technologies, artificial intelligence, and e-commerce. Every year the demand for innovative solutions and developed techs increases, which stimulates the development of these areas. Chinese ventures are investing in research and development, introducing new technologies and creating breakthrough products and services. As a result, China is becoming not only the largest consumer, but also a significant developer of technological innovations at the global level.
- Wholesale. With the drive in the purchasing power of the population, the demand for various goods and services increases, which creates favorable conditions for the registration of Chinese wholesale trade companies.
- Finance. The country's financial sector is of great interest to investors, opening up opportunities for growth in the areas of banking, investment and insurance. These sectors provide potential for increasing capital, improving financial infrastructure and introducing innovative solutions. Financiers see prospects for long-term investments in the financial sector, which offers its sustainable development and integration of modern technologies.
- Energy and ecology. Government authorities are showing interest in luring financing for the enhancement of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind energy, and the introduction of environmentally friendly techs. The administrators recognize the merit of creating favorable conditions for financiers and supporting innovative projects that contribute to environmental safety and economic growth.
Levies and accounting in China
If you are thinking about expanding your trade into the PRC market by registering a company in China , then it is advisable to deepen your knowledge of the impost system of this country. Comprehending impost obligations will help you properly plan your fiscal flows and avoid possible impost risks.
The basic income impost rate is 25%. A 15% rate applies to trades operating in occupations prompted by the state (for instance, high-tech or manufacturing enterprises). The rate for ventures specializing in the progression of software and ICs is 10%. For small trades whose annual revenue does not exceed 3 million yuan ($414,250), a preferential rate of 5% is provided for the period from January 2023 to December 2027 (inclusive).
|
Industries qualified for fifteen percent CIT rate |
|||
|
Zone |
Qualified Industries |
Operational Prerequisites |
Validity |
|
Lingang New Area (Shanghai) |
ICs, AI, Biomedicine, and Civil Aviation—or one of their sub sectors. |
|
January 1, 2020 - no deadline (ventures are competent for advantageous strategies for a maximum of 5 years following the time of the founding in the specified territory). |
|
Fujian Pingtang (Fuzhou) |
146 businesses in six primary classes:
|
|
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2025 |
|
Hengqin Zone (Zhuhai) |
150 sectors of high tech., research and advancement, tourism, etc. |
|
January 2021 - no end date. |
|
Nansha Economic Zone (Guangzhou) |
140 sectors classifications in eight categories, incorporating:
|
|
From January 1, 2022 to December 31, 2026 |
|
Qianhai Cooperation Zone (Shenzhen) |
Thirty sectors in five classifications
|
Earn at least sixty rate of your primary income from businesses in industries included in the directory of incentivized industries. |
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2025 |
|
Hainan |
143 sectors across 14 classifications, consisting:
Areas incorporated in the far-recent versions of the state Guidelines of fields motivated for global speculation and the Guidelines for Industrial Framework Adjustment. |
|
From January 1, 2020 to the furthest limit of 2025 (Hainan Streamlined commerce Port Industry Inventory is paramount until December 31, 2024). |
|
Western territories |
Sectors differ from territory to territory. |
Earn at least 60% of your primary revenue from commerce in domains incorporated in the directory of incentivized industries. |
From January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2030 |
|
Important. All suitable areas are outlined in detail in the relevant catalogues. |
|||
Withholding impost on remuneration to expats is fixed at ten percent and refers to earnings that require little to no effort, like interest. VAT is levied for the trading of commodities, excluding real estate, as well as supplying solutions for the manufacturing, restoration, and substitution of items in the territory of the PRC. The normal VAT rate is 17%, although some goods are levied at thirteen percent.
PRC imposes a venture tax on activities that include providing aids (except manufacturing, fixing, and substitute), transferring intellectual assets, and selling property. Pricing varies contingent on the type of commerce, between three percent to twenty percent.
By Chinese law, all enterprises are mandated to maintain accounting records in conformance with national accounting standards. Chinese accounting standards regulate all aspects of accounting, incorporating the preparation of financial statements, methods for valuing resources and liabilities, and reporting rules.
In addition, proper accounting can enable your organisation to effectively oversee its finances, analyze its financial position, and make informed decisions to achieve its trade goals. Receive assistance from legal experts specializing in Chinese law or request accounting services in China.
Contact our experts and get answers to your questions.
Opening an account in China
Firms with transnational founders in the PRC can initiate distinct forms of fiscal institutions, each of which has its own characteristics and potential pros and cons. The prime forms of accounts are current, savings, and speculation. Legal entities can also apply to initiate a bank account in China in foreign currency (FTN account, non-occupant account, offshore account).
There is a wide option of fiscal institutions in the jurisdiction, so it is essential to identify your goals and needs in order to select the optimal bank and account type. There are several large monetary institutions in China, such as Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Bank of China and China Construction Bank. They can offer various products and support, and also have experience working with foreign residents.
Before making a choice, it is worth examining the conditions for initiating and maintaining an account at various banks, taking into account factors such as the required minimum balance, transaction fees, availability of online banking and level of customer support.
Final Word
Registering a company with foreign capital in China shows unique opportunities for entrepreneurs who want to explore among the most dynamically developing markets in the global economy. This move could provide unprecedented opportunities for trade growth, allowing it to penetrate strategically important sectors. It also provides access to a huge pool of Chinese consumers and educated professionals. Also, it is possible to register a company in China without a visit.
IncFine experts are ready to help our clients understand the legal intricacies of Chinese legislation and provide full aid for the sequence of registering a company in China (both legal and accounting).
FAQ
Many Fortune 500 enterprises including Apple and Oracle both have businesses in Chinese territory. These brands have entered the Chinese trading field thanks to the rapidly expanding economy and are utilising it to grow worldwide. If the most reputed transnational corporations have utilised China as a platform, then both start-ups and large entrepreneurs from abroad can expect their trades to develop in the long term. Other advantages of registering a business in China:
- With 1.3 billion consumers, endeavours are guaranteed a ready market.
- The nation is positioned in the Far East, allowing easy access to sectors in neighbouring territories such as India and Japan.
- China, recognized as among the world's most rapidly growing economy ranks as one of the biggest buyers and suppliers.
- The nation presents open doors in various sectors.
There are three main options for forming a business that a non-occupant can use:
- WFOE: It is a distinct licit firm and limits the obligations of the founders to the assistance they granted to the fund. This is the primarily profitable option for transnational ventures aimed at accessing the Chinese trading field.
- Joint venture: The Chinese partner must have a controlling stake (more than 50%).
- Representative/Branch office: Only uncommercial schemes like customer support and market research are permitted.
CIT in the polity is paid at a basic rate of 25% (duty reductions authorisation for certain categories of enterprises).
The duration needed to enroll a firm in the polity differs contingent on the territory and type of an entity. Normally, the entire sequence can take from several weeks to several months. It consists of applying for name pre-approval, preparing entity records, and attaining a trade permit.



















